Introduction to Codes
Contents
Digital Data Transmission (as Maths)
- Source Alphabet - S = {s1, s1, …, sq} of q symbols
- Code Alphabet A, consisting of r symbols
- The radix r is the number of symbols in the code alphabet
- Probabilities p_i = P(S_i)
- A code that encodes each symbol s_i by a codeword (string of code symbols)
- Codewords can be seen as vectors. 1001101 corresponds to (1,0,0,1,1,0,1) \in \doubleZ_2^7
Modulo Arithmetic
If a, b are integers, and b > 0 then, a = qb + r
for unique integers q, r, with r \in {0,1,…,b-1}
Here q is the quotient and r is the remainder, we define r = a mod b
Therefore…
Integers a and b are congruent when modulo with m, and can be denoted by a === b (mod m). (a mod m) = (b mod m)
Examples
- 3+4 === 7 === 2 mod 5)
- 3-4 === -1 === 4 mod 5)
- 3x4 === 12 === 2 (mod 5)
- 3x2 === 6 === 1 (mod 5)
- 3^-1 === 2 (mod 5)
The mod n set
For binary numbers, we have the set Z2 = {0,1} modulo 2.
- 1 + 1 = 0 in mod 2
Examples
- in Z_8
- 3 + 5 = 1
- 3 - 5 = 5
- 3 x 5 = 1
- 3^-1 = 5
Linear Algebra
- A linear combination is a combination of vectors
- Vectors are linearly dependent if there is a vector can be expressed as a linear combination of the other vectors
- Else, they are linearly independent (only way to form 0 is the zero vector)
- The span is a set of all linear combinations
- The basis is a collection of linearly independent vectors that span a set of vectors
Codes
Morse Code
Morse code is a ternary code (radix of 3).
It has the symbols:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| · | dot |
| ‐ | dash |
| ⎵ | pause |
ASCII
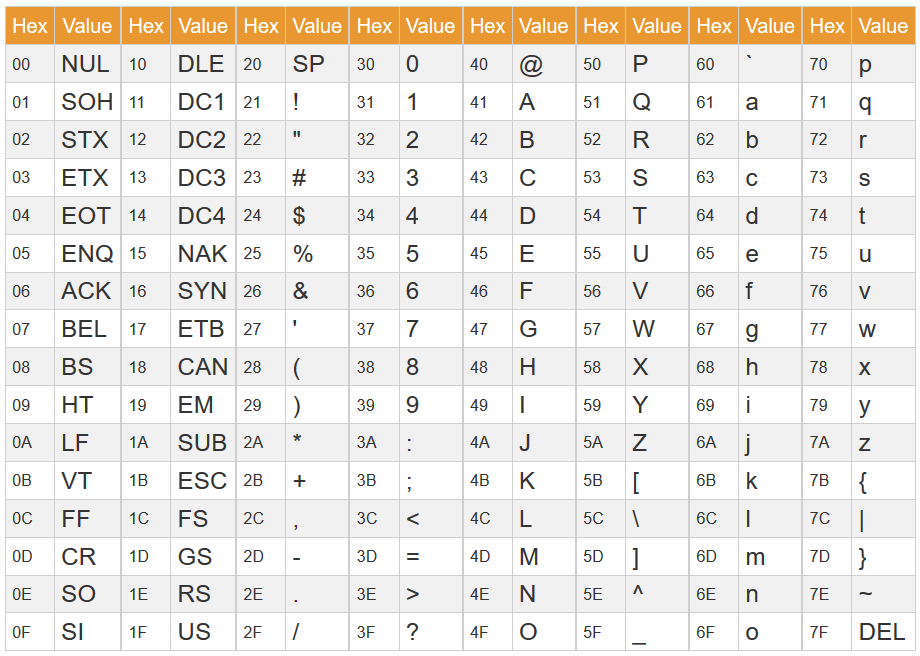
Parity / check bit
(for error detection)
The first bit of an 8 bit ASCII character can be used to partially detect errors.
Even operation - The sum of the bits should be even.
Odd operation - The sum of the bits should be odd.
Example
Suppose that we transmit 7-bit ASCII at 7x10^6 bits/s (aka 10^6 bits per second), and the probability of a given bit being in error is p = 10^-6, independently of the other bit errors
a) What is the probability of an incorrectly transmitted word?
P(errors) = 1 - P(No errors) = 1-(1-p)^7 = 7 x 10^-6
b) If a parity check were to be used, what is the new probability of an incorrectly transmitted word?
1⁄8 x (7 x 10^6) x (2.8 x 10^11) ~= 2.5 x 10^-5
Only one error every 11 hours!!!
…huh?